Understanding Intercropping: A Sustainable Coffee Farming Practice
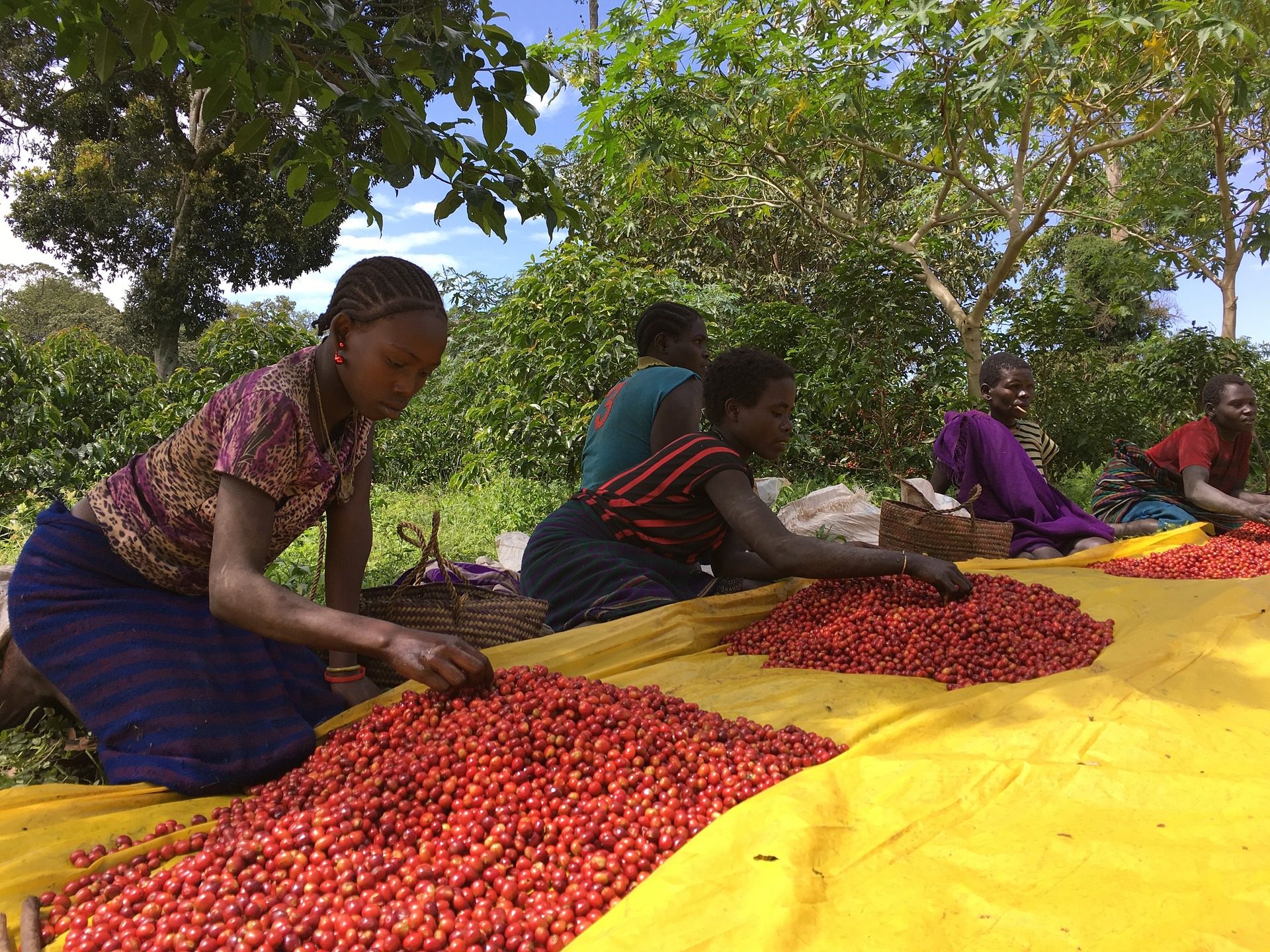
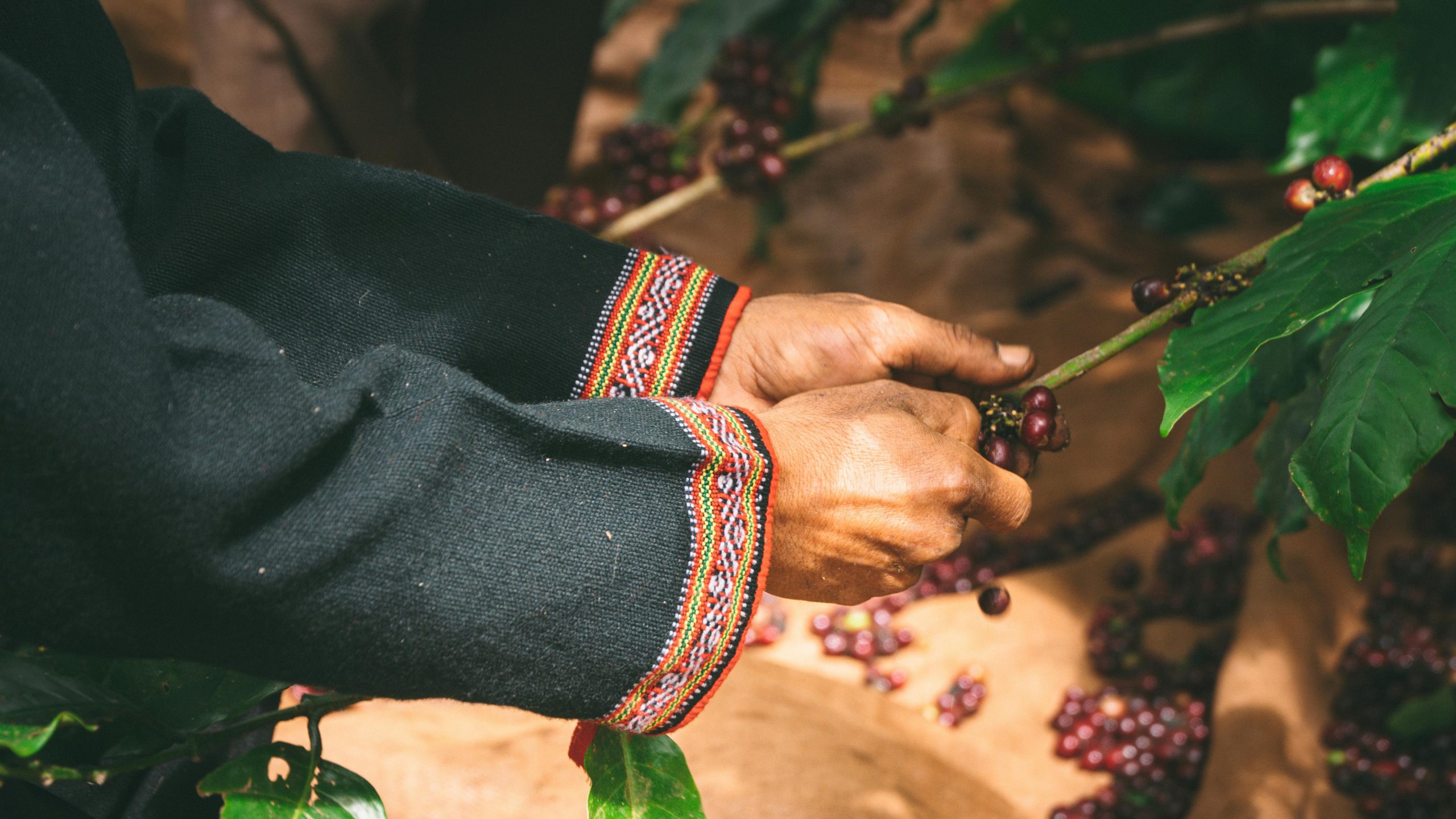
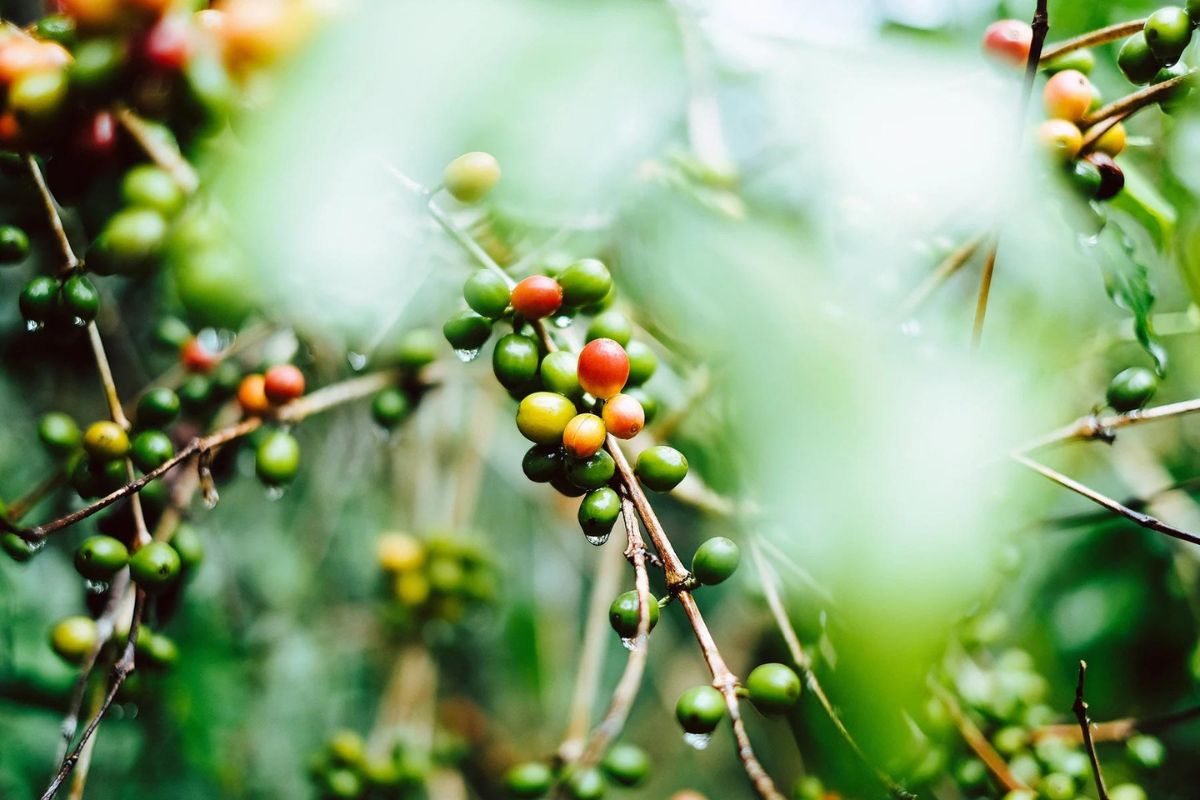
Intercropping is a method of cultivating two or more crops in proximity, allowing farmers to optimize land use while enhancing soil health. In coffee production, this method involves planting coffee trees alongside other crops such as bananas, beans, or avocados. The integration of different plant species helps create a balanced ecosystem, reducing the need for chemical fertilizers and pesticides.
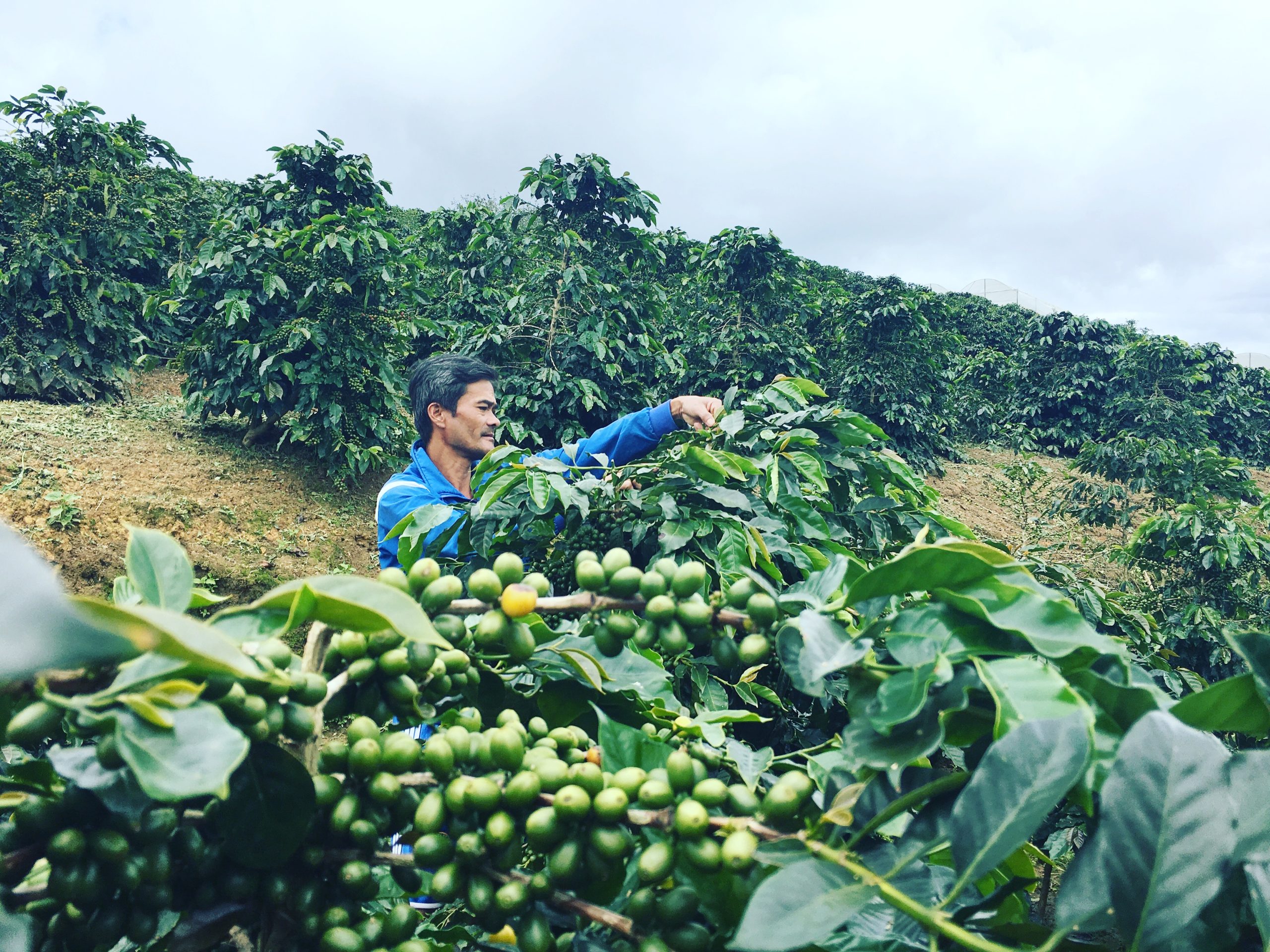

This sustainable approach is designed to combat deforestation, soil degradation, and biodiversity loss, which are often linked to traditional monoculture coffee farming. Intercropping improves soil fertility by naturally replenishing nutrients and retaining moisture, which enhances the overall productivity of the coffee plants.
CSR and Coffee Intercropping: A Commitment to Sustainability
Many corporations involved in the coffee industry have implemented CSR programs aimed at promoting intercropping as part of their sustainability efforts. These initiatives are more than just environmental responsibility; they support the social and economic well-being of coffee farmers and their communities.
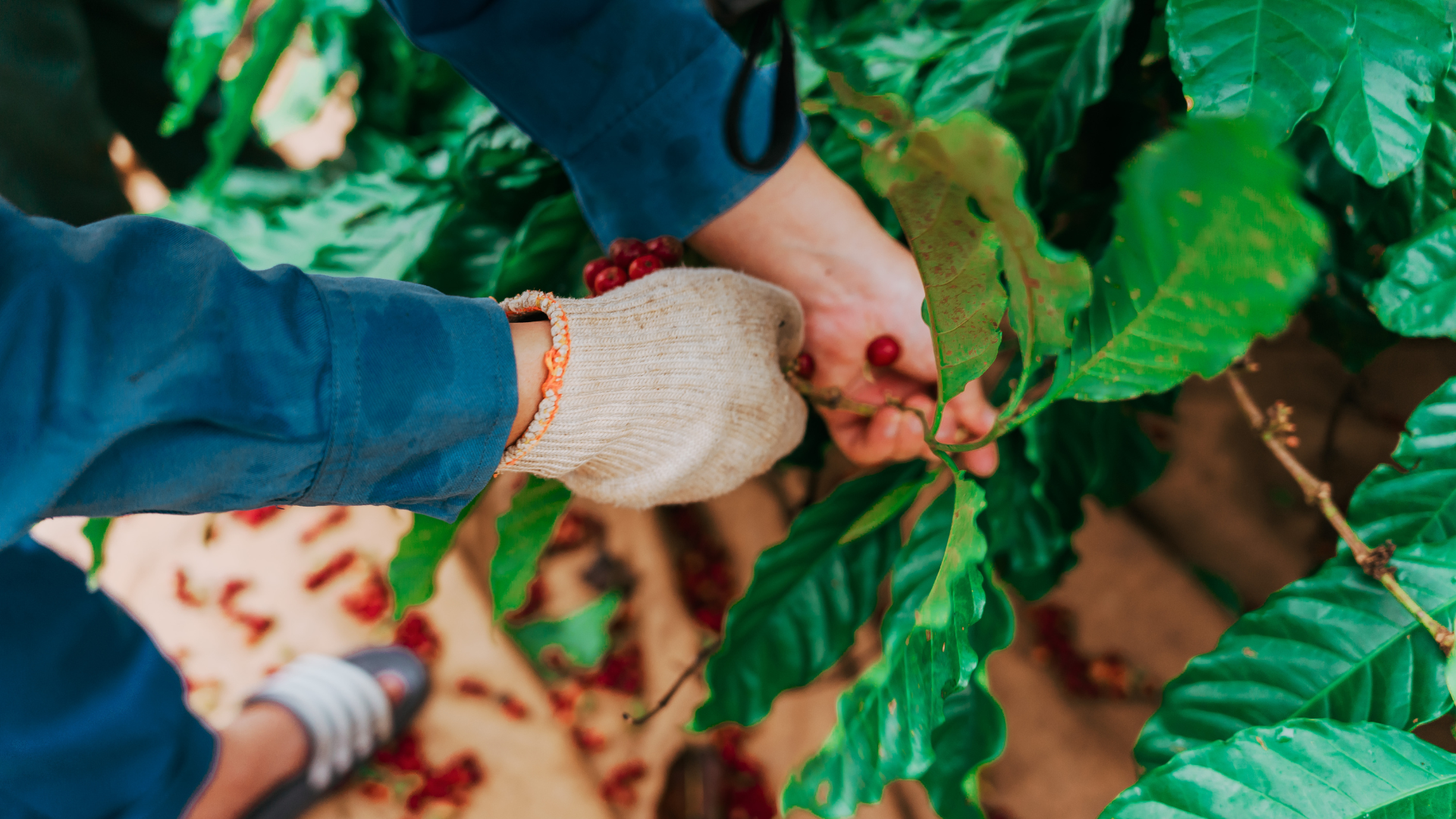

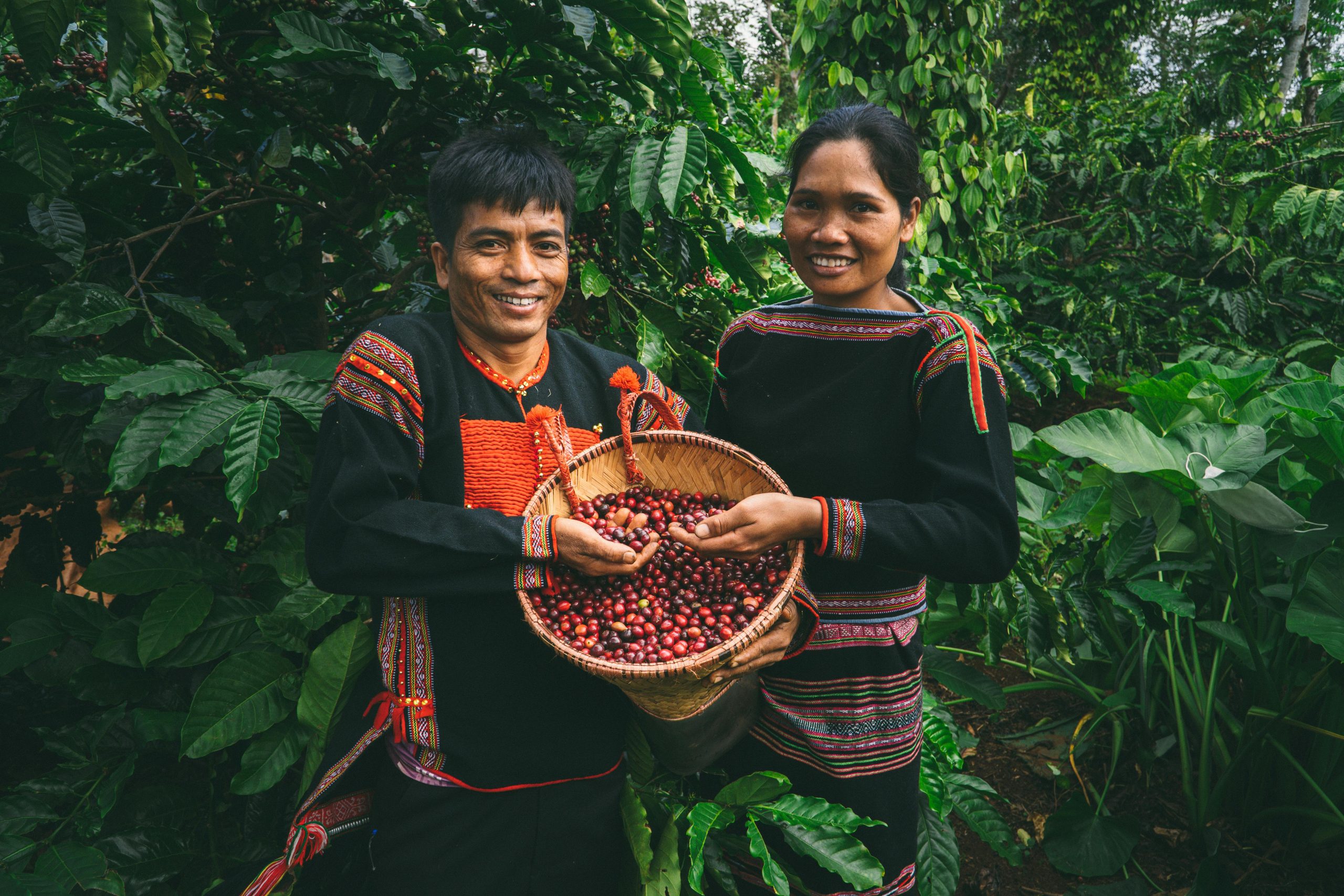
By introducing intercropping, companies help smallholder farmers diversify their income streams, reduce the risks associated with coffee price fluctuations, and improve food security. For example, growing bananas alongside coffee not only provides shade for the coffee plants but also gives farmers an additional crop to sell in local markets. This dual-cropping system ensures that farmers are less reliant on a single income source, making them more resilient to market changes.
Environmental Impact of Intercropping
One of the major benefits of intercropping is its positive impact on the environment. Traditional coffee farming, especially in large-scale monocultures, has contributed to deforestation, habitat destruction, and a significant carbon footprint. Intercropping, however, fosters biodiversity by preserving plant and animal species that thrive in diversified farming systems.
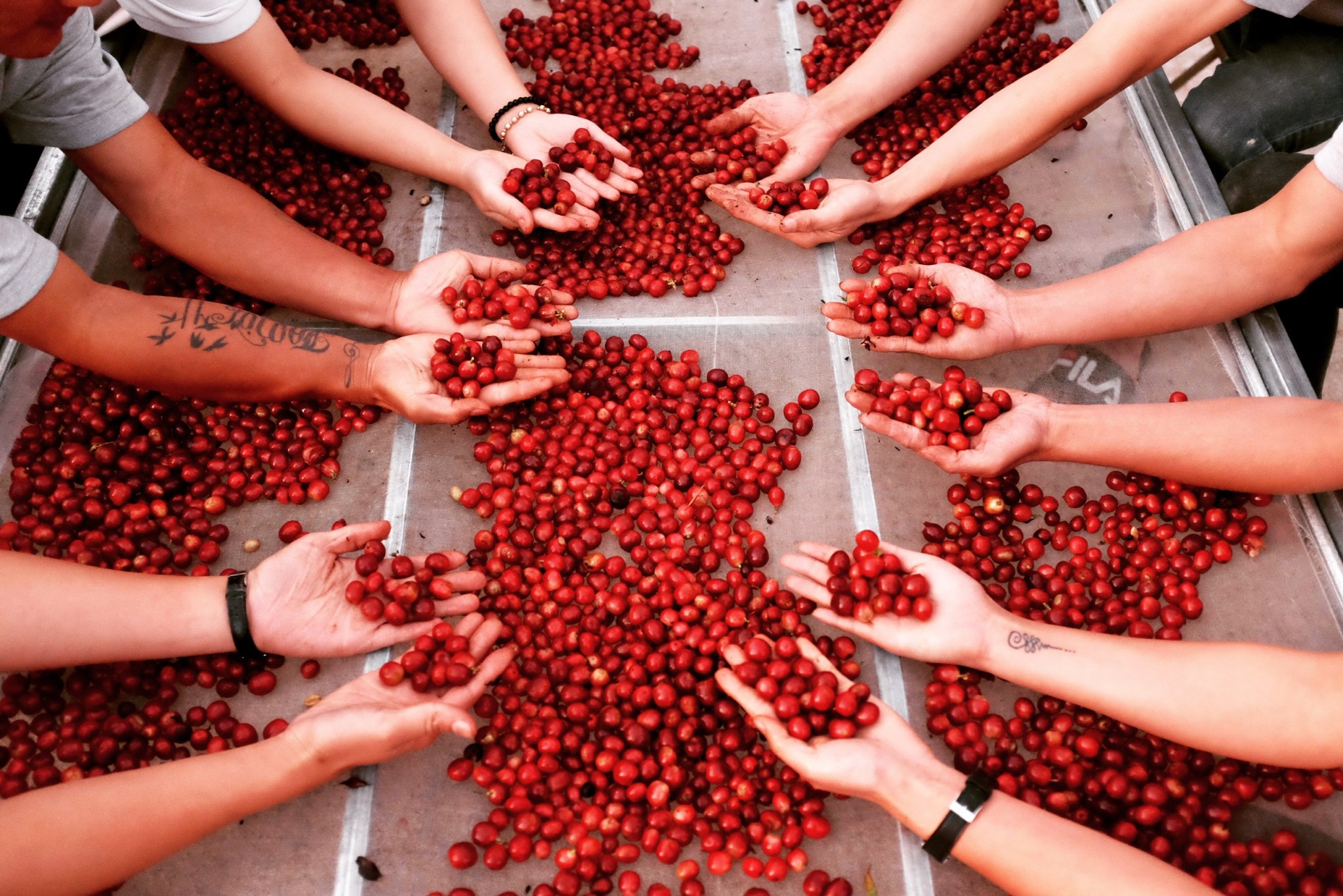

The shade provided by other crops in intercropping systems also helps in maintaining cooler temperatures and protecting coffee plants from the harsh sun, which is increasingly important as global temperatures rise due to climate change. This method enhances the carbon sequestration capacity of the land, making coffee farms more resilient and reducing their overall carbon emissions.
Community Empowerment Through CSR
Beyond environmental benefits, intercropping offers tremendous social advantages. CSR programs that promote intercropping provide training and resources to local farmers, empowering them with knowledge and tools to improve their farming practices. These programs often involve partnerships with non-governmental organizations (NGOs) and agricultural experts who offer ongoing support to farmers, ensuring the long-term success of sustainable farming initiatives.

By investing in intercropping, companies contribute to the economic development of rural communities. This method not only helps increase yields and improve food security but also creates new job opportunities. Farmers who adopt intercropping often share their success stories, encouraging others in the community to embrace sustainable practices, which fosters a ripple effect of positive change.
Intercropping coffee as part of a CSR initiative represents a powerful step towards achieving sustainability in the coffee industry. By promoting biodiversity, reducing environmental degradation, and supporting farmers' livelihoods, this approach aligns with the global call for more responsible and eco-friendly agricultural practices. Companies that invest in such sustainable initiatives demonstrate their commitment to creating lasting positive impacts on both the environment and local communities. Through intercropping, we can ensure that the future of coffee production is not only sustainable but also beneficial for generations to come.